Embark on a musical journey as we delve into the captivating world of a natural minor scale bass clef. This unique scale, with its haunting melodies and expressive intervals, unveils a realm of musical possibilities.
Bass clef, the home of low-pitched instruments, provides a canvas upon which the natural minor scale weaves its enchanting tapestry. As we explore the construction, notation, and applications of this enigmatic scale, prepare to be captivated by its evocative power.
Natural Minor Scale
The natural minor scale is a heptatonic musical scale that consists of seven different notes within an octave. It is constructed using a specific pattern of whole and half steps, giving it a distinctive sound that is often associated with melancholy or sadness.
Construction of a Natural Minor Scale
The natural minor scale is constructed by following a specific pattern of whole and half steps. Starting from the tonic (root) note, the pattern is as follows:
- Whole step
- Half step
- Whole step
- Whole step
- Half step
- Whole step
- Half step
Example of a Natural Minor Scale in Bass Clef
Here is an example of a natural minor scale in the key of A minor in bass clef:
A – G – F – E – D – C – B
Bass Clef

In musical notation, the bass clef, also known as the F clef, is a musical symbol placed at the beginning of a staff to indicate the pitches that will be played in the lower register.
The bass clef is used for instruments that typically play in the lower ranges, such as the bassoon, cello, and double bass. It is also used for the left-hand part of piano music.
A natural minor scale bass clef provides a somber and expressive foundation for musical compositions. If you’re seeking guidance in geometry, consider exploring power geometry com answer key . Returning to our musical discussion, the natural minor scale bass clef continues to captivate listeners with its evocative melodies and haunting harmonies.
Position of a Natural Minor Scale in Bass Clef
The natural minor scale can be played in any key in the bass clef. To find the notes of the natural minor scale in a particular key, follow these steps:
- Locate the tonic (first note) of the scale on the staff.
- Move up one whole step from the tonic to find the second note.
- Move down one half step from the second note to find the third note.
- Move up one whole step from the third note to find the fourth note.
- Move up one whole step from the fourth note to find the fifth note.
- Move down one half step from the fifth note to find the sixth note.
- Move up one whole step from the sixth note to find the seventh note.
For example, to play the natural minor scale in the key of C in the bass clef, the notes would be:
- C (tonic)
- D (second note)
- Eb (third note)
- F (fourth note)
- G (fifth note)
- Ab (sixth note)
- Bb (seventh note)
The natural minor scale in the key of C in the bass clef can be illustrated as follows:
|---------------------------------| |---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---| |---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---| |---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---| |---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---| |---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---| |---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---| |---|C|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Notation: A Natural Minor Scale Bass Clef
The notation of a natural minor scale in bass clef involves understanding the note names, pitches, and fingerings.
The following table illustrates the notation for each note in the natural minor scale:
Table: Natural Minor Scale Notation, A natural minor scale bass clef
| Note Name | Pitch | Fingerings |
|---|---|---|
| A | A3 | 1 |
| G | G3 | 2 |
| F | F3 | 3 |
| E | E3 | 4 |
| D | D3 | 1 |
| C | C3 | 2 |
| B | B2 | 3 |
Intervals
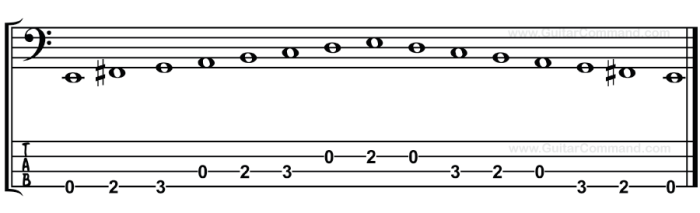
In music, an interval refers to the distance between two musical pitches. Intervals are typically measured in semitones, with a semitone representing the smallest possible interval between two adjacent notes on a standard Western musical scale. The natural minor scale, like any other musical scale, consists of a series of intervals that define its characteristic sound.
The natural minor scale comprises the following intervals:
- Root to minor second (1 semitone)
- Minor second to major third (1 semitone)
- Major third to perfect fourth (1 semitone)
- Perfect fourth to perfect fifth (1 semitone)
- Perfect fifth to minor sixth (1 semitone)
- Minor sixth to major seventh (1 semitone)
- Major seventh to octave (1 semitone)
The arrangement of these intervals creates the distinctive sound of the natural minor scale, which is often described as melancholic or somber. The presence of the minor second interval between the root and the second note, and the minor sixth interval between the sixth and seventh notes, contribute to this characteristic sound.
Musical Applications

The natural minor scale is a versatile scale with a distinctive sound that has been used in music for centuries. Its inherent emotional qualities make it a popular choice for expressing a range of emotions, from sadness and melancholy to introspection and contemplation.
The natural minor scale is often used in classical music, particularly in Baroque and Romantic era compositions. It is also commonly found in folk music, traditional music from various cultures, and popular music genres such as blues, jazz, and rock.
Musical Genres
- Classical music (Baroque, Romantic)
- Folk music
- Traditional music (various cultures)
- Blues
- Jazz
- Rock
FAQ Insights
What is a natural minor scale?
A natural minor scale is a type of musical scale that features a distinct pattern of intervals, creating a characteristic sound that is often described as haunting or melancholic.
How do I play a natural minor scale in bass clef?
To play a natural minor scale in bass clef, follow the specific fingerings and note positions Artikeld in the provided notation table.
What are some examples of how the natural minor scale is used in music?
The natural minor scale is widely used in various musical genres, including classical, jazz, and folk music. It can evoke emotions ranging from sadness and introspection to longing and nostalgia.