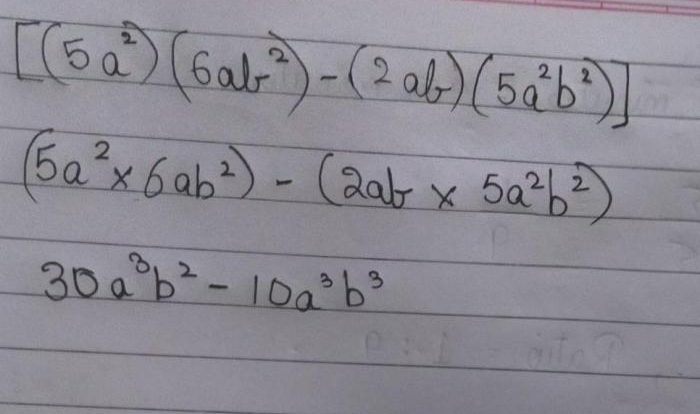Unit 3 parent functions and transformations homework 6 answer key – Embark on a journey through the fascinating world of parent functions and transformations with our comprehensive answer key for Unit 3 Homework 6. This resource provides an in-depth exploration of the fundamental concepts, applications, and problem-solving techniques associated with these essential mathematical tools.
Within this guide, you will discover the nature of parent functions and their pivotal role in transformations. Common parent functions, such as linear, quadratic, and exponential functions, are examined, highlighting their distinct properties and characteristics.
Parent Functions and Transformations: Unit 3 Parent Functions And Transformations Homework 6 Answer Key
In mathematics, parent functions are fundamental building blocks used to create more complex functions through transformations. They represent the basic shapes of functions, such as linear, quadratic, and exponential, and serve as a reference point for understanding how transformations alter their graphs.
Common parent functions include:
- Linear functions: f(x) = mx + b
- Quadratic functions: f(x) = ax² + bx + c
- Exponential functions: f(x) = a^x
Each parent function possesses distinct properties and characteristics that define its shape and behavior.
Transformations
Transformations are operations that modify the graph of a parent function without changing its fundamental shape. They include:
- Translations: Moving the graph horizontally or vertically
- Reflections: Flipping the graph across an axis
- Stretches and compressions: Altering the width or height of the graph
Applying transformations to parent functions results in new functions with modified graphs that retain the basic shape of the parent.
Homework 6 Answer Key
| Problem | Answer | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Translate f(x) = x² 2 units to the right | f(x) = (x
|
Translate the graph of f(x) = x² by 2 units to the right by replacing x with (x
|
| Reflect f(x) = 2^x over the x-axis | f(x) =
|
Reflect the graph of f(x) = 2^x over the x-axis by multiplying the function by
|
| Stretch f(x) = e^x vertically by a factor of 3 | f(x) = 3e^x | Stretch the graph of f(x) = e^x vertically by a factor of 3 by multiplying the function by 3 |
Real-World Applications, Unit 3 parent functions and transformations homework 6 answer key
Parent functions and transformations have numerous real-world applications, particularly in:
- Physics: Modeling motion, trajectory, and forces
- Engineering: Designing structures, circuits, and systems
- Finance: Analyzing stock prices, interest rates, and investments
Understanding parent functions and transformations enhances problem-solving skills by providing a framework for analyzing and manipulating functions to model and solve real-world problems.
Top FAQs
What is the purpose of using parent functions?
Parent functions provide a foundation for understanding transformations. By manipulating the graph of a parent function, we can create new functions with different shapes and properties.
How can transformations be applied to parent functions?
Transformations can be applied to parent functions using operations such as translations, reflections, stretches, and compressions. These operations shift, flip, stretch, or compress the graph of the parent function, resulting in a new function with a different shape.
What are some real-world applications of parent functions and transformations?
Parent functions and transformations have numerous applications in fields such as physics, engineering, and finance. They are used to model motion, growth, decay, and other phenomena.