Welcome to the definitive resource for understanding global migrations, where the Unit 6 Global Migrations Answer Key stands as your trusted guide. This meticulously crafted document unlocks the complexities of human movement across borders, providing a comprehensive overview of its historical, social, economic, and political dimensions.
Our journey begins with an exploration of the major global migrations that have shaped human history, from forced migrations to voluntary relocations. We will delve into the factors that have driven these movements, examining the interplay of economic disparities, political instability, and social unrest.
Historical Global Migrations: Unit 6 Global Migrations Answer Key
Throughout history, people have migrated from one place to another in search of better opportunities, to escape conflict or persecution, or to explore new lands. These migrations have shaped the world’s population distribution, cultures, and economies.
Some of the major global migrations that have occurred throughout history include:
- The Bantu expansion, which saw the Bantu-speaking peoples of Central Africa migrate south and east across the continent, displacing or absorbing other populations.
- The Mongol conquests, which led to the establishment of the Mongol Empire, the largest contiguous land empire in history.
- The European Age of Exploration, which saw European powers establish colonies and trade networks around the world, leading to the displacement and exploitation of indigenous populations.
- The Great Migration, which saw millions of African Americans move from the rural South to the urban North in the United States in the 20th century.
- The Syrian Civil War, which has caused millions of Syrians to flee their homes and seek refuge in neighboring countries and Europe.
The factors that have influenced these migrations have varied, but some of the most common include:
- Economic opportunity: People often migrate to areas where they can find better jobs and higher wages.
- Political instability: People may flee their homes due to war, persecution, or other forms of political instability.
- Environmental factors: People may migrate due to natural disasters, climate change, or other environmental factors that make their homes uninhabitable.
- Social factors: People may migrate to be closer to family or friends, or to find a more welcoming community.
Migrations have had a profound impact on the world. They have led to the spread of new ideas, technologies, and cultures, and have helped to shape the world’s political and economic landscape.
Causes of Global Migrations
Global migrations are primarily driven by economic, social, and political factors. Economic factors, such as poverty, unemployment, and low wages, often motivate people to seek better opportunities abroad. Social factors, including family reunification, cultural ties, and the desire for a better quality of life, also play a significant role in migration decisions.
Political factors, such as war, persecution, and political instability, can force people to flee their home countries and seek refuge elsewhere. Climate change and environmental disasters are also emerging as major drivers of global migration, as people are displaced due to rising sea levels, droughts, and other natural disasters.
Economic Factors
Economic factors are the most common reasons for global migrations. People migrate to countries with better economic opportunities, such as higher wages, more job opportunities, and better living standards. According to the World Bank, remittances sent by migrants to their home countries reached a record high of $589 billion in 2021, highlighting the significant economic impact of migration.
Social Factors, Unit 6 global migrations answer key
Social factors, such as family reunification, cultural ties, and the desire for a better quality of life, are also important drivers of global migration. Many people migrate to join family members who have already settled in other countries, while others seek to reconnect with their cultural roots or experience different cultures.
Political Factors
Political factors, such as war, persecution, and political instability, can force people to flee their home countries and seek refuge elsewhere. According to the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR), there were an estimated 27.1 million refugees worldwide in 2021, the highest number since World War II.
Patterns of Global Migrations
Global migrations exhibit distinct patterns that have evolved over time. These patterns involve the movement of people between specific regions and countries, influenced by a complex interplay of factors.
One notable pattern is the formation of migration corridors, which are preferred routes taken by migrants due to factors such as geographical proximity, cultural connections, and economic opportunities. Examples include the movement of people from Mexico to the United States, from North Africa to Europe, and from South Asia to the Middle East.
Another pattern is the identification of destination countries, which attract a significant number of migrants. These countries often offer favorable conditions for migrants, such as economic opportunities, political stability, and cultural tolerance. Examples include the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, Germany, and France.
Factors Influencing Migration Patterns
The patterns of global migrations are influenced by a multitude of factors, including:
- Economic factors:Disparities in economic development, job opportunities, and income levels between countries can drive migration.
- Political factors:Political instability, conflict, and persecution can compel people to seek refuge in other countries.
- Social factors:Family reunification, cultural connections, and the desire for better living conditions can motivate migration.
- Environmental factors:Natural disasters, climate change, and resource scarcity can lead to displacement and migration.
- Technological factors:Advances in transportation and communication have facilitated the movement of people across borders.
Impacts of Global Migrations
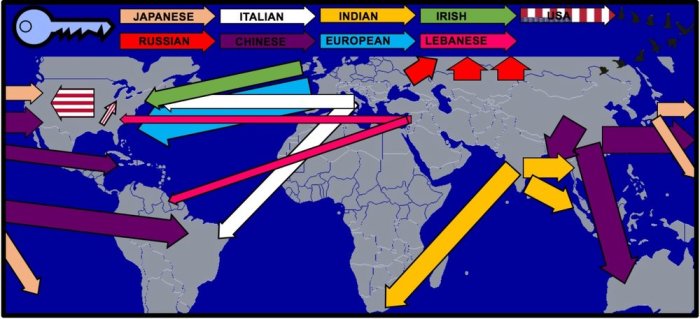
Global migrations have profound impacts on both sending and receiving countries. They can bring positive outcomes such as economic growth, cultural diversity, and social change, but also present challenges such as social tensions, discrimination, and economic inequality.
Economic Impacts
- Positive Impacts:
- Migrant workers can fill labor shortages, contributing to economic growth in receiving countries.
- Remittances sent by migrants back to their home countries can boost local economies and reduce poverty.
- Negative Impacts:
- Competition for jobs and resources can lead to lower wages and job displacement for native workers in receiving countries.
- Brain drain can occur when skilled workers leave their home countries, depriving them of valuable human capital.
Cultural Impacts
- Positive Impacts:
- Migration introduces new ideas, customs, and perspectives, enriching the cultural landscape of receiving countries.
- Cultural exchange between migrants and native populations can foster understanding and break down stereotypes.
- Negative Impacts:
- Cultural differences can sometimes lead to misunderstandings and conflicts between migrants and native populations.
- Rapid cultural change can disrupt traditional values and social norms, creating a sense of displacement for some.
Social Impacts
- Positive Impacts:
- Migration can bring new skills and perspectives to receiving countries, fostering innovation and social progress.
- Migrants often contribute to their new communities through volunteerism and civic engagement.
- Negative Impacts:
- Social tensions can arise between migrants and native populations, particularly during times of economic downturn.
- Discrimination and xenophobia can create barriers to integration and lead to social exclusion.
Contemporary Issues in Global Migrations

Contemporary global migrations are characterized by complex debates and controversies. These center around the ethical, economic, and political implications of human movement across borders.
One key issue is the tension between the rights of migrants and the sovereignty of nation-states. Proponents of open borders argue that individuals have a fundamental right to seek a better life, regardless of their origin. Conversely, those advocating for stricter border controls emphasize the need to protect national identity, cultural values, and economic stability.
Migration Policies and Practices
Countries adopt diverse approaches to migration management. Some, like the United States and Canada, have traditionally maintained relatively open immigration policies, while others, such as Japan and Saudi Arabia, have more restrictive policies.
Recent years have seen a rise in anti-immigration sentiment in many countries. This has led to increased border security measures, stricter visa requirements, and limits on refugee resettlement. However, some countries, like Germany and Sweden, have adopted more welcoming policies, recognizing the benefits that migrants can bring to their societies.
Future of Global Migrations

Global migrations are expected to continue in the coming years, driven by factors such as economic disparities, political instability, and environmental changes. The direction and magnitude of these flows will be shaped by a complex interplay of factors, including:
Economic development
Economic disparities between countries will continue to drive migration, with people moving from less developed regions to more developed ones in search of better opportunities.
Political instability
Political instability and conflict will continue to be a major factor in global migrations, with people fleeing war, persecution, and violence.
Environmental changes
Environmental changes, such as climate change and natural disasters, will increasingly displace people, forcing them to migrate to new areas.
Projections for Future Migration Patterns
Projections for future migration patterns vary depending on the assumptions made about the factors that will shape these flows. However, most projections suggest that the number of international migrants will continue to increase in the coming years.
| Year | Number of International Migrants (millions) |
|---|---|
| 2019 | 272 |
| 2030 | 305 |
| 2050 | 368 |
Factors that will Shape the Future of Global Migrations
The future of global migrations will be shaped by a complex interplay of factors, including:
Economic development
The pace of economic development in different regions of the world will influence the direction and magnitude of migration flows.
Political stability
Political stability and conflict will continue to be a major factor in global migrations.
Environmental changes
Environmental changes, such as climate change and natural disasters, will increasingly displace people, forcing them to migrate to new areas.
Technological advancements
Technological advancements will also play a role in shaping the future of global migrations. For example, the development of new communication and transportation technologies could make it easier for people to migrate.
Migration policies
Migration policies will also influence the future of global migrations. Countries that adopt more restrictive migration policies could make it more difficult for people to migrate.
Detailed FAQs
What are the major types of global migrations?
Global migrations can be classified into two broad categories: forced migrations, which are driven by factors such as war, persecution, or natural disasters; and voluntary migrations, which are motivated by economic opportunities, family reunification, or educational pursuits.
What are the key factors that influence global migrations?
The decision to migrate is often influenced by a complex interplay of economic, social, and political factors. Economic factors include income disparities, unemployment, and the search for better job opportunities. Social factors include family reunification, cultural ties, and the desire for a better quality of life.
Political factors include war, persecution, and political instability.
What are the positive and negative impacts of global migrations?
Global migrations can have both positive and negative impacts on both sending and receiving countries. Positive impacts include increased economic growth, cultural diversity, and the transfer of skills and knowledge. Negative impacts can include social tensions, xenophobia, and the strain on public resources.